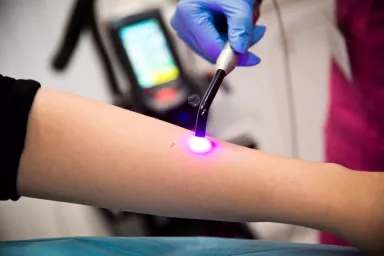
PIGMENT SPOT TREATMENT IS PERFORMED BETWEEN NOVEMBER AND FEBRUARY
More and more people are struggling with pigment spots. The causes of hyperpigmentation can vary — hormonal changes, inflammation, skin burns, or exposure to sunlight. Treatment can improve age spots, sun pigmentation, freckles, and even discolored scars. Before the procedure, the pigmentation must be evaluated to determine whether it is suitable for laser treatment. In addition to laser therapy, pigmentation can also be treated with a chemical peel, carefully selected by the doctor.
Details
Hyperpigmentation is characterized as a disorder in the production or distribution of pigment, resulting in darkening of the skin. The size and shape of the affected area can vary greatly and are not determining diagnostic features.
Pigmentation disorders most commonly involve basic physiological pigments such as melanin, hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin), or carotene.
Hyperpigmentation can also be a symptom of other pathological conditions — most often certain metabolic diseases, which may lead to abnormal production or accumulation of colored substances such as hemosiderin, bilirubin, or homogentisic acid. These diseases are relatively rare, and such pigmentation disorders are not commonly encountered.
Fortunately, in most cases, hyperpigmentation is only a cosmetic issue. The most common type is melanin hyperpigmentation. The skin pigment melanin is the key factor in determining skin color. It is produced by specialized cells — melanocytes — located in the basal layer of the epidermis. The starting material for melanin production is the amino acid tyrosine, which is converted into melanin through a series of metabolic reactions.
The number of melanocytes is approximately the same in all people; what differs is the intensity of melanin production. Based on the level of pigmentation, the skin phototype is then determined.
Congenital hyperpigmentation
Congenital depigmentation manifests as freckles. It is genetically determined and occurs mainly in red-haired or fair-haired individuals (the so-called Celtic type). It typically appears in the central part of the face, on the arms, and in the upper third of the chest or back.
Acquired hyperpigmentation
Melanin hyperpigmentation more commonly affects people with higher phototypes. It is most often seen in middle-aged women, but its incidence is also increasing in men (who generally do not consider it a significant cosmetic issue).
Hyperpigmentation usually does not have a single cause but is rather a complex process. The most common type is chloasma, which arises from a combination of UV exposure and hormonal fluctuations (e.g. pregnancy, oral contraceptives), the use of certain cosmetic products, or specific medications.
Pigmentation changes occur in up to 10–20% of women of reproductive age using hormonal contraception, which is why this group should pay special attention to prevention.
The fundamental approach is to eliminate the cause that triggers hyperpigmentation. Because melanin production is the skin’s natural response to UV radiation, pigment spots may reappear quickly after new sun exposure.
It is important to remember that all sources of UV radiation (sunlight, tanning beds, or artificial light sources) can cause pigmentation. It’s not just intentional sunbathing — any exposure counts. Even through glass (at home, in the office, or in the car), a significant portion of UVA radiation passes through.
Just a few minutes of exposure can trigger uneven melanin activation in predisposed individuals. Therefore, proper UV protection is crucial — especially on highly exposed areas such as the face and décolleté.
Whitening of pigment spots
Skin whitening is a long-term process that requires regular care and consistent sun protection.
In 1961, hydroquinone began to be used for whitening melanin pigment spots. Hydroquinone blocks the key enzyme that converts tyrosine into the melanin precursor dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). However, it cannot remove existing pigment — it only prevents new formation. Long-term use was therefore required.
Experience has shown that hydroquinone can also block pigmentation in areas outside the application site, leading to unwanted hypopigmentation elsewhere. Long-term use can even cause paradoxical darkening (so-called exogenous ochronosis). For this reason, hydroquinone has been banned in bleaching creams in the EU since 2000.
Another option is a chemical peel, which removes the outermost skin layers along with superficial pigment cells. It does not affect deeper pigmentation. Peels are performed using acids such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or trichloroacetic acid. Only a few products are suitable for home use; in most cases, treatment must be performed by a dermatologist. Aggressive application may damage deeper skin layers.
A more recent approach involves dioic acids (e.g. octadecenedioic acid, azelaic acid). These substances inhibit melanin production and promote even distribution in the skin, gradually blending the border between hyperpigmented and normal skin. Their main advantage is excellent tolerance, making them safe for home use.
Among physical methods, intense pulsed light (IPL) and special lasers are commonly used. IPL therapy leads to photo-rejuvenation, improving skin texture and removing unwanted cosmetic imperfections. Specific lasers target pigment-containing cells through selective photothermolysis, effectively breaking down discolored areas.
Price list
| Medik8 peel for acne-prone skin | from 1,500 CZK |
| Medik8 peel for pigmentation spots | from 1,500 CZK |
| Medik8 peel for skin rejuvenation | from 1,500 CZK |
| Medical peel | 1,600–2,000 CZK |
| Removal of skin tags | 800 - 1.600 Kč |
| Odstranění kožních lézí (cena dle rozsahu) | 700 - 1.100 Kč |
| Removal of pigmentation (depends on size) | from 1.000 Kč |
| Removal of spider veins on face | 500 Kč - 2.000 Kč |
| Removal of spider veins on legs | 1.000 - 2.500 Kč |
| Removal of hemangioma | 500 - 1.500 Kč |
| Rejuvenation | 1.200 Kč |
| Treatment of onychomadesis | 2.000 Kč |
| Removal of scars | 800 - 1.500 Kč |
| Removal of acne scars | from 3.000 Kč |
| Removal of stretchmarks | from 3.000 Kč |
| Acne treatment | 2.500 Kč (1 body part) |
| Herpes treatment | od 500 Kč |
| Treatment of old wound scars | od 500 Kč |
The prices above are for illustrative purposes only. The final price will be determined by our doctors during your consultation.